# These are all the modules we'll be using later. Make sure you can import them
# before proceeding further.
from __future__ import print_function
import numpy as np
import tensorflow as tf
from six.moves import cPickle as pickle
First reload the data we generated in notmist.ipynb.
pickle_file = 'notMNIST.pickle'
with open(pickle_file, 'rb') as f:
save = pickle.load(f)
train_dataset = save['train_dataset']
train_labels = save['train_labels']
valid_dataset = save['valid_dataset']
valid_labels = save['valid_labels']
test_dataset = save['test_dataset']
test_labels = save['test_labels']
del save # hint to help gc free up memory
print('Training set', train_dataset.shape, train_labels.shape)
print('Validation set', valid_dataset.shape, valid_labels.shape)
print('Test set', test_dataset.shape, test_labels.shape)
Reformat into a shape that's more adapted to the models we're going to train:
- data as a flat matrix,
- labels as float 1-hot encodings.
image_size = 28
num_labels = 10
def reformat(dataset, labels):
dataset = dataset.reshape((-1, image_size * image_size)).astype(np.float32)
# Map 2 to [0.0, 1.0, 0.0 ...], 3 to [0.0, 0.0, 1.0 ...]
labels = (np.arange(num_labels) == labels[:,None]).astype(np.float32)
return dataset, labels
train_dataset, train_labels = reformat(train_dataset, train_labels)
valid_dataset, valid_labels = reformat(valid_dataset, valid_labels)
test_dataset, test_labels = reformat(test_dataset, test_labels)
print('Training set', train_dataset.shape, train_labels.shape)
print('Validation set', valid_dataset.shape, valid_labels.shape)
print('Test set', test_dataset.shape, test_labels.shape)
Problem 1¶
Introduce and tune L2 regularization for both logistic and neural network models. Remember that L2 amounts to adding a penalty on the norm of the weights to the loss. In TensorFlow, you can compute the L2 loss for a tensor t using nn.l2_loss(t). The right amount of regularization should improve your validation / test accuracy.
Multinomial logistic regression with L2 loss function
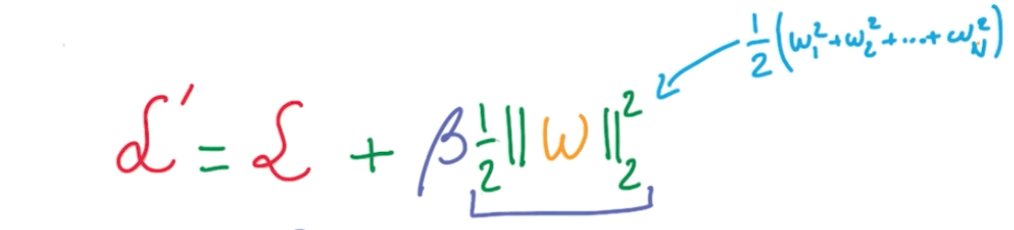
- Load Data & Build Computation Graph
# This is to expedite the process
train_subset = 10000
# This is a good beta value to start with
beta = 0.01
graph = tf.Graph()
with graph.as_default():
# Input data.
# They're all constants.
tf_train_dataset = tf.constant(train_dataset[:train_subset, :])
tf_train_labels = tf.constant(train_labels[:train_subset])
tf_valid_dataset = tf.constant(valid_dataset)
tf_test_dataset = tf.constant(test_dataset)
# Variables
# They are variables we want to update and optimize.
weights = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([image_size * image_size, num_labels]))
biases = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([num_labels]))
# Training computation.
logits = tf.matmul(tf_train_dataset, weights) + biases
# Original loss function
loss = tf.reduce_mean(tf.nn.softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(logits, tf_train_labels) )
# Loss function using L2 Regularization
regularizer = tf.nn.l2_loss(weights)
loss = tf.reduce_mean(loss + beta * regularizer)
# Optimizer.
optimizer = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(0.5).minimize(loss)
# Predictions for the training, validation, and test data.
train_prediction = tf.nn.softmax(logits)
valid_prediction = tf.nn.softmax( tf.matmul(tf_valid_dataset, weights) + biases )
test_prediction = tf.nn.softmax(tf.matmul(tf_test_dataset, weights) + biases)
- Run Computation & Iterate
num_steps = 801
def accuracy(predictions, labels):
return (100.0 * np.sum(np.argmax(predictions, 1) == np.argmax(labels, 1))
/ predictions.shape[0])
with tf.Session(graph=graph) as session:
# This is a one-time operation which ensures the parameters get initialized as
# we described in the graph: random weights for the matrix, zeros for the
# biases.
tf.initialize_all_variables().run()
print('Initialized')
for step in range(num_steps):
# Run the computations. We tell .run() that we want to run the optimizer,
# and get the loss value and the training predictions returned as numpy
# arrays.
_, l, predictions = session.run([optimizer, loss, train_prediction])
if (step % 100 == 0):
print('Loss at step {}: {}'.format(step, l))
print('Training accuracy: {:.1f}'.format(accuracy(predictions,
train_labels[:train_subset, :])))
# Calling .eval() on valid_prediction is basically like calling run(), but
# just to get that one numpy array. Note that it recomputes all its graph
# dependencies.
# You don't have to do .eval above because we already ran the session for the
# train_prediction
print('Validation accuracy: {:.1f}'.format(accuracy(valid_prediction.eval(),
valid_labels)))
print('Test accuracy: {:.1f}'.format(accuracy(test_prediction.eval(), test_labels)))
Neural Network with L2 Regularization
- 1 Hidden Layer using RELUs
num_nodes= 1024
batch_size = 128
beta = 0.01
graph = tf.Graph()
with graph.as_default():
# Input data. For the training data, we use a placeholder that will be fed
# at run time with a training minibatch.
tf_train_dataset = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, shape=(batch_size, image_size * image_size))
tf_train_labels = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, shape=(batch_size, num_labels))
tf_valid_dataset = tf.constant(valid_dataset)
tf_test_dataset = tf.constant(test_dataset)
# Variables.
weights_1 = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([image_size * image_size, num_nodes]))
biases_1 = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([num_nodes]))
weights_2 = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([num_nodes, num_labels]))
biases_2 = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([num_labels]))
# Training computation.
logits_1 = tf.matmul(tf_train_dataset, weights_1) + biases_1
relu_layer= tf.nn.relu(logits_1)
logits_2 = tf.matmul(relu_layer, weights_2) + biases_2
# Normal loss function
loss = tf.reduce_mean(tf.nn.softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(logits_2, tf_train_labels))
# Loss function with L2 Regularization with beta=0.01
regularizers = tf.nn.l2_loss(weights_1) + tf.nn.l2_loss(weights_2)
loss = tf.reduce_mean(loss + beta * regularizers)
# Optimizer.
optimizer = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(0.5).minimize(loss)
# Predictions for the training
train_prediction = tf.nn.softmax(logits_2)
# Predictions for validation
logits_1 = tf.matmul(tf_valid_dataset, weights_1) + biases_1
relu_layer= tf.nn.relu(logits_1)
logits_2 = tf.matmul(relu_layer, weights_2) + biases_2
valid_prediction = tf.nn.softmax(logits_2)
# Predictions for test
logits_1 = tf.matmul(tf_test_dataset, weights_1) + biases_1
relu_layer= tf.nn.relu(logits_1)
logits_2 = tf.matmul(relu_layer, weights_2) + biases_2
test_prediction = tf.nn.softmax(logits_2)
num_steps = 3001
with tf.Session(graph=graph) as session:
tf.initialize_all_variables().run()
print("Initialized")
for step in range(num_steps):
# Pick an offset within the training data, which has been randomized.
# Note: we could use better randomization across epochs.
offset = (step * batch_size) % (train_labels.shape[0] - batch_size)
# Generate a minibatch.
batch_data = train_dataset[offset:(offset + batch_size), :]
batch_labels = train_labels[offset:(offset + batch_size), :]
# Prepare a dictionary telling the session where to feed the minibatch.
# The key of the dictionary is the placeholder node of the graph to be fed,
# and the value is the numpy array to feed to it.
feed_dict = {tf_train_dataset : batch_data, tf_train_labels : batch_labels}
_, l, predictions = session.run([optimizer, loss, train_prediction], feed_dict=feed_dict)
if (step % 500 == 0):
print("Minibatch loss at step {}: {}".format(step, l))
print("Minibatch accuracy: {:.1f}".format(accuracy(predictions, batch_labels)))
print("Validation accuracy: {:.1f}".format(accuracy(valid_prediction.eval(), valid_labels)))
print("Test accuracy: {:.1f}".format(accuracy(test_prediction.eval(), test_labels)))
Problem 2¶
Let's demonstrate an extreme case of overfitting. Restrict your training data to just a few batches. What happens?
Continuing from the Neural Network with L2 Regularization above
num_steps = 3001
train_dataset_2 = train_dataset[:500, :]
train_labels_2 = train_labels[:500]
with tf.Session(graph=graph) as session:
tf.initialize_all_variables().run()
print("Initialized")
for step in range(num_steps):
# Pick an offset within the training data, which has been randomized.
# Note: we could use better randomization across epochs.
offset = (step * batch_size) % (train_labels_2.shape[0] - batch_size)
# Generate a minibatch.
batch_data = train_dataset_2[offset:(offset + batch_size), :]
batch_labels = train_labels_2[offset:(offset + batch_size), :]
# Prepare a dictionary telling the session where to feed the minibatch.
# The key of the dictionary is the placeholder node of the graph to be fed,
# and the value is the numpy array to feed to it.
feed_dict = {tf_train_dataset : batch_data, tf_train_labels : batch_labels}
_, l, predictions = session.run([optimizer, loss, train_prediction], feed_dict=feed_dict)
if (step % 500 == 0):
print("Minibatch loss at step {}: {}".format(step, l))
print("Minibatch accuracy: {:.1f}".format(accuracy(predictions, batch_labels)))
print("Validation accuracy: {:.1f}".format(accuracy(valid_prediction.eval(), valid_labels)))
print("Test accuracy: {:.1f}".format(accuracy(test_prediction.eval(), test_labels)))
As you can see, there's high training accuracy but low validation accuracy. There is overfitting here.
Problem 3¶
Introduce Dropout on the hidden layer of the neural network. Remember: Dropout should only be introduced during training, not evaluation, otherwise your evaluation results would be stochastic as well. TensorFlow provides nn.dropout() for that, but you have to make sure it's only inserted during training.
What happens to our extreme overfitting case?
num_nodes= 1024
batch_size = 128
beta = 0.01
graph = tf.Graph()
with graph.as_default():
# Input data. For the training data, we use a placeholder that will be fed
# at run time with a training minibatch.
tf_train_dataset = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, shape=(batch_size, image_size * image_size))
tf_train_labels = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, shape=(batch_size, num_labels))
tf_valid_dataset = tf.constant(valid_dataset)
tf_test_dataset = tf.constant(test_dataset)
# Variables.
weights_1 = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([image_size * image_size, num_nodes]))
biases_1 = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([num_nodes]))
weights_2 = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([num_nodes, num_labels]))
biases_2 = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([num_labels]))
# Training computation.
logits_1 = tf.matmul(tf_train_dataset, weights_1) + biases_1
relu_layer= tf.nn.relu(logits_1)
# Dropout on hidden layer: RELU layer
keep_prob = tf.placeholder("float")
relu_layer_dropout = tf.nn.dropout(relu_layer, keep_prob)
logits_2 = tf.matmul(relu_layer_dropout, weights_2) + biases_2
# Normal loss function
loss = tf.reduce_mean(tf.nn.softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(logits_2, tf_train_labels))
# Loss function with L2 Regularization with beta=0.01
regularizers = tf.nn.l2_loss(weights_1) + tf.nn.l2_loss(weights_2)
loss = tf.reduce_mean(loss + beta * regularizers)
# Optimizer.
optimizer = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(0.5).minimize(loss)
# Predictions for the training
train_prediction = tf.nn.softmax(logits_2)
# Predictions for validation
logits_1 = tf.matmul(tf_valid_dataset, weights_1) + biases_1
relu_layer= tf.nn.relu(logits_1)
logits_2 = tf.matmul(relu_layer, weights_2) + biases_2
valid_prediction = tf.nn.softmax(logits_2)
# Predictions for test
logits_1 = tf.matmul(tf_test_dataset, weights_1) + biases_1
relu_layer= tf.nn.relu(logits_1)
logits_2 = tf.matmul(relu_layer, weights_2) + biases_2
test_prediction = tf.nn.softmax(logits_2)
num_steps = 3001
with tf.Session(graph=graph) as session:
tf.initialize_all_variables().run()
print("Initialized")
for step in range(num_steps):
# Pick an offset within the training data, which has been randomized.
# Note: we could use better randomization across epochs.
offset = (step * batch_size) % (train_labels.shape[0] - batch_size)
# Generate a minibatch.
batch_data = train_dataset[offset:(offset + batch_size), :]
batch_labels = train_labels[offset:(offset + batch_size), :]
# Prepare a dictionary telling the session where to feed the minibatch.
# The key of the dictionary is the placeholder node of the graph to be fed,
# and the value is the numpy array to feed to it.
feed_dict = {tf_train_dataset : batch_data, tf_train_labels : batch_labels, keep_prob : 0.5}
_, l, predictions = session.run([optimizer, loss, train_prediction], feed_dict=feed_dict)
if (step % 500 == 0):
print("Minibatch loss at step {}: {}".format(step, l))
print("Minibatch accuracy: {:.1f}".format(accuracy(predictions, batch_labels)))
print("Validation accuracy: {:.1f}".format(accuracy(valid_prediction.eval(), valid_labels)))
print("Test accuracy: {:.1f}".format(accuracy(test_prediction.eval(), test_labels)))
Extreme Overfitting
num_steps = 3001
beta = 0.01
train_dataset_2 = train_dataset[:500, :]
train_labels_2 = train_labels[:500]
with tf.Session(graph=graph) as session:
tf.initialize_all_variables().run()
print("Initialized")
for step in range(num_steps):
# Pick an offset within the training data, which has been randomized.
# Note: we could use better randomization across epochs.
offset = (step * batch_size) % (train_labels_2.shape[0] - batch_size)
# Generate a minibatch.
batch_data = train_dataset_2[offset:(offset + batch_size), :]
batch_labels = train_labels_2[offset:(offset + batch_size), :]
# Prepare a dictionary telling the session where to feed the minibatch.
# The key of the dictionary is the placeholder node of the graph to be fed,
# and the value is the numpy array to feed to it.
feed_dict = {tf_train_dataset : batch_data, tf_train_labels : batch_labels, keep_prob : 0.5}
_, l, predictions = session.run([optimizer, loss, train_prediction], feed_dict=feed_dict)
if (step % 500 == 0):
print("Minibatch loss at step {}: {}".format(step, l))
print("Minibatch accuracy: {:.1f}".format(accuracy(predictions, batch_labels)))
print("Validation accuracy: {:.1f}".format(accuracy(valid_prediction.eval(), valid_labels)))
print("Test accuracy: {:.1f}".format(accuracy(test_prediction.eval(), test_labels)))
Problem 4¶
Try to get the best performance you can using a multi-layer model! The best reported test accuracy using a deep network is 97.1%.
One avenue you can explore is to add multiple layers.
Another one is to use learning rate decay:
global_step = tf.Variable(0) # count the number of steps taken.
learning_rate = tf.train.exponential_decay(0.5, global_step, ...)
optimizer = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(learning_rate).minimize(loss, global_step=global_step)
Model
- 5 hidden layers NN
- RELUs
- Number of nodes decrease by 50% with each hidden layer that is deeper in the neural net
- Overfitting measures
- L2 Regularization
- Learning rate (beta) with exponential decay
- Dropout
- L2 Regularization
- 10,000 steps
import math as math
batch_size = 128
beta = 0.001
hidden_nodes_1 = 1024
hidden_nodes_2 = int(hidden_nodes_1 * 0.5)
hidden_nodes_3 = int(hidden_nodes_1 * np.power(0.5, 2))
hidden_nodes_4 = int(hidden_nodes_1 * np.power(0.5, 3))
hidden_nodes_5 = int(hidden_nodes_1 * np.power(0.5, 4))
graph = tf.Graph()
with graph.as_default():
'''Input Data'''
# For the training data, we use a placeholder that will be fed
# at run time with a training minibatch.
tf_train_dataset = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, shape=(batch_size, image_size * image_size))
tf_train_labels = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, shape=(batch_size, num_labels))
tf_valid_dataset = tf.constant(valid_dataset)
tf_test_dataset = tf.constant(test_dataset)
'''Variables'''
# Hidden RELU layer 1
weights_1 = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([image_size * image_size, hidden_nodes_1], stddev=math.sqrt(2.0/(image_size*image_size))))
biases_1 = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([hidden_nodes_1]))
# Hidden RELU layer 2
weights_2 = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([hidden_nodes_1, hidden_nodes_2], stddev=math.sqrt(2.0/hidden_nodes_1)))
biases_2 = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([hidden_nodes_2]))
# Hidden RELU layer 3
weights_3 = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([hidden_nodes_2, hidden_nodes_3], stddev=math.sqrt(2.0/hidden_nodes_2)))
biases_3 = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([hidden_nodes_3]))
# Hidden RELU layer 4
weights_4 = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([hidden_nodes_3, hidden_nodes_4], stddev=math.sqrt(2.0/hidden_nodes_3)))
biases_4 = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([hidden_nodes_4]))
# Hidden RELU layer 5
weights_5 = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([hidden_nodes_4, hidden_nodes_5], stddev=math.sqrt(2.0/hidden_nodes_4)))
biases_5 = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([hidden_nodes_5]))
# Output layer
weights_6 = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([hidden_nodes_5, num_labels], stddev=math.sqrt(2.0/hidden_nodes_5)))
biases_6 = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([num_labels]))
'''Training computation'''
# Hidden RELU layer 1
logits_1 = tf.matmul(tf_train_dataset, weights_1) + biases_1
hidden_layer_1 = tf.nn.relu(logits_1)
# Dropout on hidden layer: RELU layer
keep_prob = tf.placeholder("float")
hidden_layer_1_dropout = tf.nn.dropout(hidden_layer_1, keep_prob)
# Hidden RELU layer 2
logits_2 = tf.matmul(hidden_layer_1_dropout, weights_2) + biases_2
hidden_layer_2 = tf.nn.relu(logits_2)
# Dropout on hidden layer: RELU layer
hidden_layer_2_dropout = tf.nn.dropout(hidden_layer_2, keep_prob)
# Hidden RELU layer 3
logits_3 = tf.matmul(hidden_layer_2_dropout, weights_3) + biases_3
hidden_layer_3 = tf.nn.relu(logits_3)
# Dropout on hidden layer: RELU layer
hidden_layer_3_dropout = tf.nn.dropout(hidden_layer_3, keep_prob)
# Hidden RELU layer 4
logits_4 = tf.matmul(hidden_layer_3_dropout, weights_4) + biases_4
hidden_layer_4 = tf.nn.relu(logits_4)
# Dropout on hidden layer: RELU layer
hidden_layer_4_dropout = tf.nn.dropout(hidden_layer_4, keep_prob)
# Hidden RELU layer 5
logits_5 = tf.matmul(hidden_layer_4_dropout, weights_5) + biases_5
hidden_layer_5 = tf.nn.relu(logits_5)
# Dropout on hidden layer: RELU layer
hidden_layer_5_dropout = tf.nn.dropout(hidden_layer_5, keep_prob)
# Output layer
logits_6 = tf.matmul(hidden_layer_5_dropout, weights_6) + biases_6
# Normal loss function
loss = tf.reduce_mean(tf.nn.softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(logits_6, tf_train_labels))
# Loss function with L2 Regularization with decaying learning rate beta=0.5
regularizers = tf.nn.l2_loss(weights_1) + tf.nn.l2_loss(weights_2) + \
tf.nn.l2_loss(weights_3) + tf.nn.l2_loss(weights_4) + \
tf.nn.l2_loss(weights_5) + tf.nn.l2_loss(weights_6)
loss = tf.reduce_mean(loss + beta * regularizers)
'''Optimizer'''
# Decaying learning rate
global_step = tf.Variable(0) # count the number of steps taken.
start_learning_rate = 0.5
learning_rate = tf.train.exponential_decay(start_learning_rate, global_step, 100000, 0.96, staircase=True)
optimizer = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(learning_rate).minimize(loss, global_step=global_step)
# Predictions for the training
train_prediction = tf.nn.softmax(logits_6)
# Predictions for validation
valid_logits_1 = tf.matmul(tf_valid_dataset, weights_1) + biases_1
valid_relu_1 = tf.nn.relu(valid_logits_1)
valid_logits_2 = tf.matmul(valid_relu_1, weights_2) + biases_2
valid_relu_2 = tf.nn.relu(valid_logits_2)
valid_logits_3 = tf.matmul(valid_relu_2, weights_3) + biases_3
valid_relu_3 = tf.nn.relu(valid_logits_3)
valid_logits_4 = tf.matmul(valid_relu_3, weights_4) + biases_4
valid_relu_4 = tf.nn.relu(valid_logits_4)
valid_logits_5 = tf.matmul(valid_relu_4, weights_5) + biases_5
valid_relu_5 = tf.nn.relu(valid_logits_5)
valid_logits_6 = tf.matmul(valid_relu_5, weights_6) + biases_6
valid_prediction = tf.nn.softmax(valid_logits_6)
# Predictions for test
test_logits_1 = tf.matmul(tf_test_dataset, weights_1) + biases_1
test_relu_1 = tf.nn.relu(test_logits_1)
test_logits_2 = tf.matmul(test_relu_1, weights_2) + biases_2
test_relu_2 = tf.nn.relu(test_logits_2)
test_logits_3 = tf.matmul(test_relu_2, weights_3) + biases_3
test_relu_3 = tf.nn.relu(test_logits_3)
test_logits_4 = tf.matmul(test_relu_3, weights_4) + biases_4
test_relu_4 = tf.nn.relu(test_logits_4)
test_logits_5 = tf.matmul(test_relu_4, weights_5) + biases_5
test_relu_5 = tf.nn.relu(test_logits_5)
test_logits_6 = tf.matmul(test_relu_5, weights_6) + biases_6
test_prediction = tf.nn.softmax(test_logits_6)
num_steps = 15000
with tf.Session(graph=graph) as session:
tf.initialize_all_variables().run()
print("Initialized")
for step in range(num_steps):
# Pick an offset within the training data, which has been randomized.
# Note: we could use better randomization across epochs.
offset = (step * batch_size) % (train_labels.shape[0] - batch_size)
# Generate a minibatch.
batch_data = train_dataset[offset:(offset + batch_size), :]
batch_labels = train_labels[offset:(offset + batch_size), :]
# Prepare a dictionary telling the session where to feed the minibatch.
# The key of the dictionary is the placeholder node of the graph to be fed,
# and the value is the numpy array to feed to it.
feed_dict = {tf_train_dataset : batch_data, tf_train_labels : batch_labels, keep_prob : 0.5}
_, l, predictions = session.run([optimizer, loss, train_prediction], feed_dict=feed_dict)
if (step % 500 == 0):
print("Minibatch loss at step {}: {}".format(step, l))
print("Minibatch accuracy: {:.1f}".format(accuracy(predictions, batch_labels)))
print("Validation accuracy: {:.1f}".format(accuracy(valid_prediction.eval(), valid_labels)))
print("Test accuracy: {:.1f}".format(accuracy(test_prediction.eval(), test_labels)))